Menstruation and Women Health
Menstruation
Menstruationis the release of endometrial tissue and blood that occurs as part of the menstrual cycle. This cycle is controlled by hormones produced in both the brain and ovaries and prepares the reproductive organs for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the lining begins to break down and discharges from the body through the vagina as the menstrual period.
Menstrual disorders involve the absence of menses (amenorrhea) and abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Menstrual symptoms include the following;
- Menstrual cramps
- Ovulation pain
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
Menstruation usually start when women are around 12 or 13 years old (puberty) and continues until menopause (around 50 years old ). These are considered as woman’s reproductive years and indicate a woman is physically able to become pregnant. Menstrual periods usually occur once a month and last for 3-7 days during each month. A missed menstrual period is frequently the first signal of pregnancy has occurred. The uterine lining is not shed, but rather will grow during pregnancy and develop into the placenta (a temporary organ that provides nourishment for the developing embryo). Missed periods may also indicate the presence of other gynecological problems, such as hormonal or endocrine disorders.
Eumenorrhea denotes normal, regular menstruation that lasts for 3 to 5 days, (but anywhere from 2 to 7 days is considered normal). The average blood loss during menstruation is around 35 millilitres with 10-80 mL considered normal, many women also notice shedding of the endometrium lining that appears as tissue mixed with the blood. Sometimes this is erroneously thought to indicate an early-term miscarriage of an embryo. An enzyme called plasmin — contained in the endometrium — tends to inhibit the blood from clotting.
Majority of women typically use sanitary napkins (pads) or tampons to absorb menstrual flow. Before and during menstruation, women may experience some mild to moderate cramps, water retention and irritability.
Physical experience
In many women, various intense sensations brought about by the involved hormones and by cramping of the uterus can precede or accompany menstruation. Stronger sensations may include significant menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea), abdominal pain, migraine headaches, depression, emotional sensitivity, feeling bloated, and changes in sex drive. Breast discomfort caused by premenstrual water retention or hormone fluctuation is very common. The sensations experienced vary from woman to woman and from month to month.
Emotional reactions
Some women may experience emotional side-effects. Their emotion look like quite unstable. These range from the irritability popularly associated with Premenstrual Syndrome , tiredness, depress or "weepiness" (i.e. tears of emotional closeness).
Flow
The normal menstrual flow follows a "crescendo-decrescendo" pattern; that is, it starts at a moderate level, increases somewhat, and then slowly tapers. Sudden heavy flows or amounts in excess of 80 mL (hypermenorrhea or menorrhagia) may stem from hormonal disturbance, uterine abnormalities, including uterine leiomyoma or cancer, and other causes.
Duration
The typical woman bleeds for two to seven days at the beginning of each menstrual cycle. Prolonged bleeding (metrorrhagia, also meno-metrorrhagia) no longer shows a clear interval pattern. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is hormonally caused bleeding abnormalities, typically anovulation. All these bleeding abnormalities need medical attention; they may indicate hormone imbalances, uterine fibroids, or other problems. As pregnant patients may bleed, a pregnancy test forms part of the evaluation of abnormal bleeding.
Menstruation Cycle
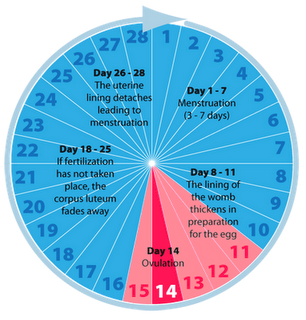
Day 1 -7: Menstruation - Normally 3-7 days.
Every woman's cycle (the time from the first day of your menstrual period until the first day of your next menstrual period) is different. On average, a woman has her menstrual period for 3-7 days. The average length of a woman's cycle is 28-32 days. This leaves plenty of room for a woman to vary from her neighbor, friend, or co-worker. Women also vary in the severity of symptoms that occur before and during menstruation.
Approximately 85% of women who menstruate report changes in the days or weeks before their menstruation that cause problems that affect their normal lives. This is known as Premenstrual Syndrome .
During menstruation, the uterus, which is a muscle, contracts and relaxes more than it does at other times in the month. This can produce the uncomfortable feeling of cramps. Using a heating pad or hot water bottle may help ease some of the discomfort. Taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as naproxen, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen may also help. Other discomforts during menstruation may include breast tenderness, bloating, headaches, fatigue, mood swings, and food cravings. Some women will experience these symptoms more than others will, and not every woman will experience all of these symptoms.
Hormones trigger your ovaries to produce and release one egg from either your right or your left ovary. This is called ovulation. Before ovulation occurs, your uterine lining is thickening to prepare for a fertilized egg to implant in the uterus. If an egg is not fertilized, then the uterine lining sheds. This is called menstruation or your menstrual period.
Day 12 -18: Ovulation
Ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from the ovary, pushed down the fallopian tube and is available to be fertilized. The lining of the uterus has thickened to prepare for a fertilized egg.
Day 18-25: If fertilization has not taken place, the corpus luteum fades away.
Day 26 -28: The uterine lining detaches leading to menstruation.
Vaginal infections or vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that creates discharge, odor, irritation or itching. Three vaginal infections are the most common. Their causes are quite different, their symptoms similar, and treatment varies.
i. Bacterial vaginosis ii. Vaginal yeast infection iii. Trichomoniasis.
Vaginal Infection Symptoms
Vaginal Discharge
The things to be worried about include if the discharge has a yellow or green color, is clumpy like cottage cheese, or has a bad odor.
Different Types of Discharge
White:
Thick and white discharge is common during menstrual cycle. Normal white discharge is not accompanied by itching. If itching is present, thick white discharge can indicate a yeast infection.
Clear and stretchy:
This is "fertile" mucous and means women are ovulating.
Clear and watery:
This occurs at different times of women menstrual cycle and can be particularly heavy after exercising.
Yellow or Green:
Yellow or Green discharge indicates a vaginal infection, especially if clumpy or thick like cottage cheese or has a foul odor.
Brown:
This may happen right after periods and is just "cleaning out" your vaginal. Old blood looks brown.
Spotting Blood/Brown Discharge:
This may occur when you are ovulating/mid-cycle. Sometimes early in pregnancy you may have spotting or a brownish discharge at the time your period would normally come. If you have spotting at the time of your normal period rather than your usual amount of flow and you have had sex without using birth control, you should check a pregnancy test.
A normal vaginal discharge consists of about a teaspoon a day that is white or transparent, thick to thin and odorless. This is formed by the normal bacteria and fluids the vaginal cells put off. The discharge can be more noticeable at different times of the month depending on ovulation, menstrual flow, sexual activity and birth control.
It is not uncommon for the normal discharge to be dark, brown or discolored a day or two following the menstrual period.
If you are having following symptoms, please get advice from your doctor.
- Itching
- Pain
- Discomfort
- Rash or sores alone or with a vaginal discharge
Sanitary Napkins (Pads) and Vaginal Infection/Discharge

The physical discomforts of menstruation experienced by every women is a vital sign of good health and fertility that indicates the body’s ability to reproduce – an amazing phenomenon of nature since the beginning of time that is vital for existence of the human race.
Hence, the women’s menstrual cycle is a very venerable and sacred affair!
Menstruation, Vaginal Infection and Sanitary Napkins
- The chances of matured women to be affected by vaginal infections are as high as 83%.
- The use of poor quality sanitary napkins caused 62% of the women to be infected. Sanitary napkins, classified as fast moving consumer goods (FMCG), disposed after use. Manufacturers will have the tendency to use recycle paper as raw material to save on the cost of production. Large amount of chemical are required for the recycle process to bleach, sterilize and remove odours from these recycle papers.
- One the average, a woman needs about 3 to 6 days a month for the treatment of vaginal infections.
Common mistakes of the use of sanitary napkins
- Use of unwashed hand throughout the whole process of handling the napkins.
- Storing sanitary napkins in moist area, such as bathroom.
- Using expired sanitary napkins.
- Selecting sanitary napkins without consider the quality of the sanitary napkins.
- Using medicated or deodorized sanitary napkins.
- Sanitary napkin is not changed regularly.
Common symptoms of bacterial infection during mentruation
- Fever.
- External Vaginal inflammation
- Itchy
- Vaginal Inflammation
- Cervical Inflammation
- Endometrial Inflammation
- Excessive white discharge
- Searing heat or pain in the lower abdomen
Fever, nauseous, urge to urinate, urinal pain, sore waist, aching waist and fatigue are symptoms of bacterial infections during menstruation, which may lead to more threatening gynecological diseases.
Bacterial Infections during menstruation
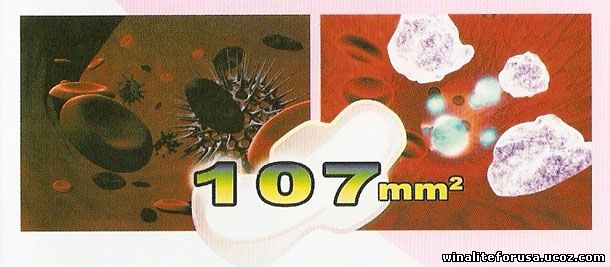
After continuous usage of normal sanitary napkins for 2 hours, it’s surface will be a conducive breeding ground for bacteria. As much as 107 bacteria per mm2 can reside on surface of the common sanitary napkin.
Video : Menstruation and Women Heal








